5. Lagopus software switch on KVM Virtual Machine¶
This section describes:
- How to install Lagopus on KVM-based virtual machine.
- Example configuration to run Lagopus software switch as Layer 2 switch using Ryu as an OpenFlow controller.
- Lagopus with raw-socket mode will be used.
5.1. Software Versions¶
- Lagopus software switch: Lagopus software switch 0.2.10
- OS: Linux Ubuntu Server 14.04.3 LTS
5.2. Overall topology and client host setup¶
In this example, we will connect two client hosts to Lagopus software switch bridge ports.
- KVM VM running Lagopus software switch, client hosts, and bridges to connect them are all created on KVM host.
- Client hosts are created using network namespace (netns) for simplicity.
- You can also create and use KVM VM as client host instead of netns.
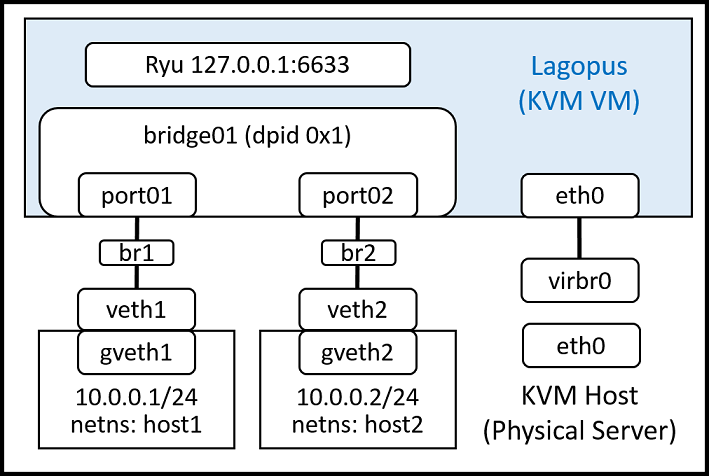
5.3. Setup client hosts and bridges on KVM host¶
edit
/etc/network/interfacesto setup vethpair, netns and bridge.reboot to apply the changes you just made.
Note
sudo /etc/init.d/networking restartdoes not work on Ubuntu 14.04.$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces $ cat /etc/network/interfaces auto veth1 iface veth1 inet manual pre-up ip link add veth1 type veth peer name gveth1 pre-up ip netns add host1 pre-up ip link set gveth1 netns host1 pre-up ip netns exec host1 ip link set gveth1 up pre-up ip netns exec host1 ip addr add 10.0.0.1/24 brd + dev gveth1 post-down ip link del veth1 auto veth2 iface veth2 inet manual pre-up ip link add veth2 type veth peer name gveth2 pre-up ip netns add host2 pre-up ip link set gveth2 netns host2 pre-up ip netns exec host2 ip link set gveth2 up pre-up ip netns exec host2 ip addr add 10.0.0.2/24 brd + dev gveth2 post-down ip link del veth2 auto br1 br2 iface br1 inet manual bridge_ports veth1 iface br2 inet manual bridge_ports veth2
Confirm bridges are created and interfaces are connected.
$ brctl show bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br1 8000.a2b53bff4545 no veth1 br2 8000.fe7797ec6779 no veth2 virbr0 8000.000000000000 yes
Confirm IP address is correctly configured on client hosts (gveth1/gveth2).
$ sudo ip netns exec host1 ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 9: gveth1@if10: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state LOWERLAYERDOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether c2:5f:77:74:3e:97 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.0.0.1/24 brd 10.0.0.255 scope global gveth1 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever $ sudo ip netns exec host2 ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 11: gveth2@if12: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state LOWERLAYERDOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether ca:6a:eb:34:3c:f0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.0.0.2/24 brd 10.0.0.255 scope global gveth2 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
5.4. KVM installation and VM creation (Ubuntu)¶
Details about installing and running KVM on Ubuntu, refer to ubuntu documentation: KVM/Installation .
5.4.1. KVM installation¶
KVM requires CPU supporting Intel VT or AMD-V. Confirm it with below command.
It’s supported if result was 1 or more. Not supported if 0 (zero).
$ egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo 4 $
Install necessary packages. (listed below)
reboot and log in.
Check installation was completed using
virshandlsmod.$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-bin ubuntu-vm-builder bridge-utils virtinst $ sudo reboot ... after reboot and log in... $ virsh version Compiled against library: libvirt 1.2.2 Using library: libvirt 1.2.2 Using API: QEMU 1.2.2 Running hypervisor: QEMU 2.0.0 $ lsmod | grep kvm kvm_intel 163840 0 kvm 507904 1 kvm_intel
5.4.2. VM creation using virt-install¶
There are two different options to create VM on headless server, virt-install and vmbuilder. The difference is vmbuilder is for creating Ubuntu-based guests, whereas virt-install lets you install other kinds of operationg systems, which are other Linux distributions and other OS like Windows, FreeBSD etc.
Note
There used to be a command called “Ubuntu-vm-builder”, which is now a wrapper to vmbuilder. It’s now only maintained for compatibility wih previous scripts, thus recommend using vmbuilder.
Download ISO image of Ubuntu Server. (in
~/img)$ mkdir ~/img $ cd ~/img ~/img$ wget http://ftp.riken.jp/Linux/ubuntu-releases/14.04.4/ubuntu-14.04.3-server-amd64.iso
Create VM (use
--dry-runto check without actually creating VM)$ sudo virt-install \ --name lagopus \ --ram 4096 \ --disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/lagopus.img,size=30 \ --vcpus 2 \ --cpu host \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant ubuntutrusty \ --virt-type=kvm \ --noautoconsole \ -c ~/img/ubuntu-14.04.3-server-amd64.iso \ --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0,password=vnc Starting install... Allocating 'lagopus.img' | 30 GB 00:00 Creating domain... | 0 B 00:00 Domain installation still in progress. You can reconnect to the console to complete the installation process. (Confirm VM was created successfully) $ virsh list Id Name State ---------------------------------------------------- 4 lagopus running
Continue OS (Ubuntu) installation on the VM.
- Check vnc display number assigned to the newly created VM.
- Connect to the VM via VNC. <kvm-host-ip>:<vnc-display>
$ virsh vncdisplay lagopus :0 # VNC display number is "0" for above case. # Continue installation by connecting via VNC.
Start VM after OS installation.
VM will shut down after installing OS and would not start automatically by default.
Note
Hostname of the VM was set as lagopus-kvm in this example.
$ virsh list --all Id Name State ---------------------------------------------------- - lagopus shut off $ virsh start lagopus Domain lagopus started $ virsh list --all Id Name State ---------------------------------------------------- 4 lagopus running
5.4.3. Connecting to VM via SSH from KVM host (Usermode Networking)¶
By default, VM will have interface automatically connected to a bridge created local to KVM host. (ex: “virbr0”)
This is called “Usermode Networking”, where you can:
Access external network from VM via host (NAT).
Connect to VM from host via SSH.
To connect to VM from host via SSH:
Connect to VM via VNC and confirm IP address assigned to it.
$ ssh <VM-usermode-interface-ip>from KVM host.
5.4.4. Adding network interface to VM¶
Confirm existing network interfaces on VM (named “lagopus”).
$ virsh domiflist lagopus Interface Type Source Model MAC ------------------------------------------------------- - network default virtio 52:54:00:6a:f2:f8
Add two interfaces to VM. (use different MAC address)
Script to generate MAC address.
$ vi genmac.sh #!/bin/bash # generate a random mac address for the qemu nic printf '52:54:00:%02x:%02x:%02x\n' $((RANDOM%256)) $((RANDOM%256)) $((RANDOM%256)) example: $ ./genmac.sh 52:54:00:f0:bd:b1
virsh command to add interfaces to VM.
$ virsh attach-interface --domain lagopus --type bridge \ --source br1 --model virtio \ --mac 52:54:00:f0:bd:b1 --config --live Interface attached successfully $ virsh attach-interface --domain lagopus --type bridge \ --source br2 --model virtio \ --mac 52:54:00:0f:69:9c --config --live Interface attached successfully
Options:
--domain name of the VM you wan to add interface
--source bridge on KVM host to connect the interface
--type type of interface: network, bridge
--model NIC model: virtio, e1000 etc.
--mac MAC address of the interface
--config flag to make it persistant after VM reboot
--live flag to apply change immediately on a running VM
Confirm interfaces are created and connected to bridge “br1” and “br2”.
$ virsh domiflist lagopus Interface Type Source Model MAC ------------------------------------------------------- vnet0 network default virtio 52:54:00:6a:f2:f8 vnet1 bridge br1 virtio 52:54:00:f0:bd:b1 vnet2 bridge br2 virtio 52:54:00:0f:69:9c $ brctl show bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br1 8000.a2b53bff4545 no veth1 vnet1 br2 8000.fe54000f699c no veth2 vnet2 virbr0 8000.fe54006af2f8 yes vnet0
Connect to VM (via SSH)
Confirm two interfaces (eth1/eth2) were added.
$ ssh <vm-ip-address> <usr>@<vm-ip-address>'s password: lagopus-kvm:~$ ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 52:54:00:6a:f2:f8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.122.224/24 brd 192.168.122.255 scope global eth0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fe6a:f2f8/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether 52:54:00:f0:bd:b1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff 4: eth2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether 52:54:00:0f:69:9c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff lagopus-kvm:~$ ethtool -i eth1 driver: virtio_net version: 1.0.0 firmware-version: bus-info: 0000:00:06.0 supports-statistics: no supports-test: no supports-eeprom-access: no supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: no
Make newly added interface (eth1/eth2) permanetly up during boot.
Note
you don’t need to assign IP address to Lagopus ports.
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces # add below lines auto eth1 iface eth1 inet manual up ip link set eth1 up down ip link set eth1 down auto eth2 iface eth2 inet manual up ip link set eth2 up down ip link set eth2 down
reboot or manually apply setting by
ifupcommand.Note
sudo /etc/init.d/networking restartdoes not work on Ubuntu 14.04.lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo ifup eth1 lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo ifup eth2
5.5. Lagopus installation steps on KVM VM¶
Proceed following steps inside the VM.
Note
all operations in this section are done INSIDE the VM
5.5.1. Installing Lagopus to VM (raw socket)¶
Install necessary packages. (described below)
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo apt-get install build-essential libexpat-dev libgmp-dev \ libssl-dev libpcap-dev byacc flex git \ python-dev python-pastedeploy python-paste python-twisted
Download Lagopus software switch source code.
lagopus-kvm:~$ git clone -b v0.2.10 --recursive https://github.com/lagopus/lagopus.gitCompile and install Lagopus software switch with raw-socket mode
lagopus-kvm:~$ ./configure --disable-dpdk lagopus-kvm:~$ make lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo make install
5.5.2. Setup Lagopus configuration¶
Copy sample configuration file under
/usr/local/etc/lagopus/.lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo mkdir /usr/local/etc/lagopus/ lagopus-kvm:~$ cd ~/lagopus lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo cp misc/examples/lagopus.dsl /usr/local/etc/lagopus/lagopus.dsl
Edit
lagopus.dsl* Example:- One OpenFlow controller: “127.0.0.1”
eth0: Management interface. (Thus does not appear in the configuration)eth1,eth2are used as Lagopus dataplane port. These two port are accessed with raw-socket mode.
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo vi /usr/local/etc/lagopus/lagopus.dsl channel channel01 create -dst-addr 127.0.0.1 -protocol tcp controller controller01 create -channel channel01 -role equal -connection-type main interface interface01 create -type ethernet-rawsock -device eth1 interface interface02 create -type ethernet-rawsock -device eth2 port port01 create -interface interface01 port port02 create -interface interface02 bridge bridge01 create -controller controller01 -port port01 1 -port port02 2 -dpid 0x1 bridge bridge01 enable lagopus-kvm:~$
Run Lagopus software switch
Confirm two interfaces are recognized.
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo lagopus lagopus-kvm:~$ lagosh Lagosh> show version { "product-name": "Lagopus", "version": "0.2.2-release" } Lagosh> Lagosh> show interface [ { "name": "interface01", "rx-dropped": 0, "is-enabled": true, "tx-errors": 0, "rx-bytes": 0, "tx-packets": 0, "rx-packets": 0, "tx-bytes": 0, "rx-errors": 0, "tx-dropped": 0 }, { "name": "interface02", "rx-dropped": 0, "is-enabled": true, "tx-errors": 0, "rx-bytes": 0, "tx-packets": 0, "rx-packets": 0, "tx-bytes": 0, "rx-errors": 0, "tx-dropped": 0 } ]
Stop Lagopus software switch and exit lagosh.
Lagosh> stop Lagosh> exit lagopus-kvm:~$
5.6. Building Layer 2 switch using Ryu as an OpenFlow controller¶
5.6.1. Setup Ryu Simple switch¶
Install necessary packages.
Use pip command and install Ryu.
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo apt-get install python-setuptools python-pip python-dev \ libxml2-dev libxslt-dev lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo pip install ryu
Run below only if required.
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo pip install oslo.config lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo pip install six --upgrade
Run simple_switch Ryu application.
lagopus-kvm:~$ ryu-manager --verbose /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/ryu/app/simple_switch_13.pyOpen new SSH connection and run Lagopus software switch.
lagopus-kvm:~$ sudo lagopusConfirm Lagopus is connected to Ryu from ryu-manager console log.
connected socket:<eventlet.greenio.base.GreenSocket object at 0x7f9c71c1bb50> address:('127.0.0.1', 35705) hello ev <ryu.controller.ofp_event.EventOFPHello object at 0x7f9c71bad1d0> move onto config mode EVENT ofp_event->SimpleSwitch13 EventOFPSwitchFeatures switch features ev version=0x4,msg_type=0x6,msg_len=0x20,xid=0xb0597afd,OFPSwitchFeatures(auxiliary_id=0,capabilities=79,datapath_id=1,n_buffers=65535,n_tables=255) move onto main mode
5.6.2. Confirm ping works via Lagopus software switch¶
On KVM host, ping between namespace host1/host2.
$ sudo ip netns exec host1 ping 10.0.0.2 PING 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=11.5 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.745 ms ... $ sudo ip netns exec host2 ping 10.0.0.1 PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.770 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.798 ms ...